Diesel generator sets, widely used in shipping, telecommunications, and other vital sectors of the national economy, serve as primary, backup, or emergency AC power sources. In recent years, power shortages caused by uneven economic development and resource distribution—particularly in southern coastal regions—have underscored the critical role of diesel generators in sustaining economic growth.
Technological advancements have transformed these units from manually operated, attended systems to automated (self-starting, unmanned, remote-controlled/monitored), low-emission, and low-noise solutions. Modern diesel generator sets are characterized by their flexibility, convenience, high automation, quiet operation, and reduced emissions. Innovations in engineering continue to enhance their durability, reliability, stability, and environmental performance, meeting increasingly stringent societal demands.
(1) Composition
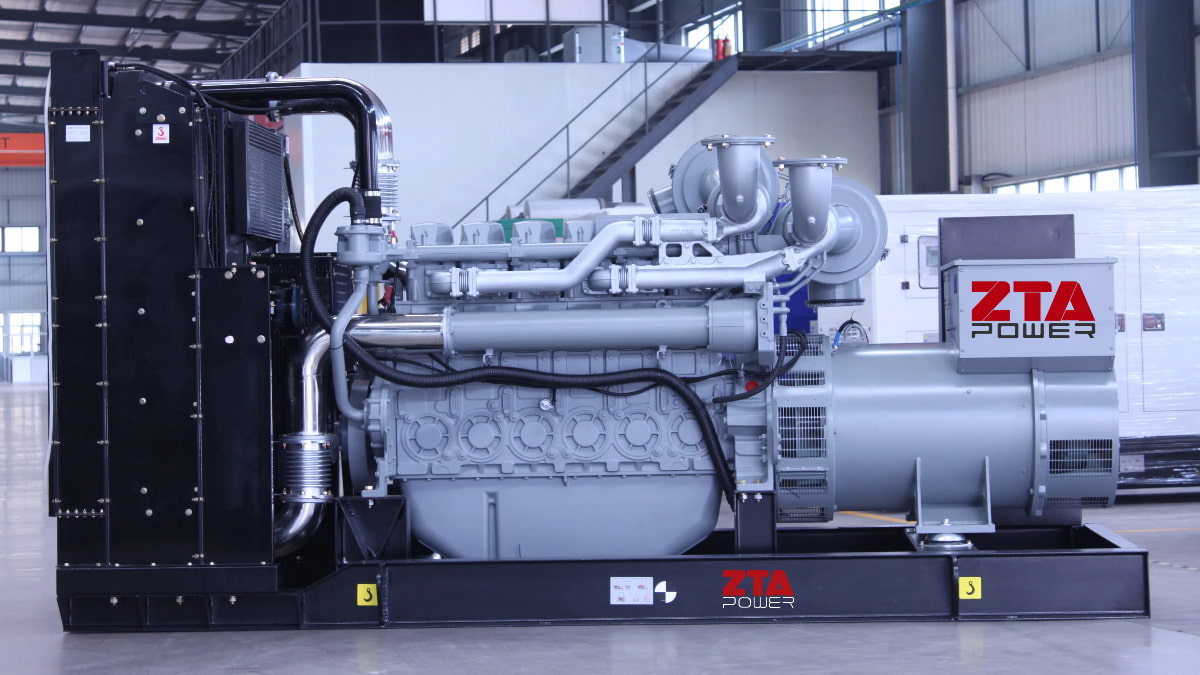
A diesel generator set—a type of internal combustion power unit—comprises three core components:
1.Diesel Engine
2.Three-Phase AC Synchronous Generator
3.Control System (including automatic monitoring, control, and protection devices).
Mobile Units: The diesel engine, generator, and control panel are mounted on a shared chassis.
Large Fixed Units: The engine and generator are installed on a welded steel base anchored to a reinforced concrete foundation, with separate control systems and fuel tanks.
The generator connects to the diesel engine via a cylindrical flexible coupling, ensuring alignment between the engine crankshaft and generator rotor within specified tolerances. To minimize noise, specialized silencers are installed, and full soundproofing may be applied for sensitive environments. Vibration dampers or rubber pads are typically used between major components (engine, generator, radiator, control panel) and the chassis.
(2) Classification and Functions
Diesel generator sets vary by structure, control mode, and protection features. Key types include:
1. Standard Units
The most common configuration includes:
Auto-Start Units
Enhancements over standard units:
Automatically starts upon grid power failure
PLC-Controlled Automated Units
Advanced systems feature:
High-performance diesel engine + brushless generator
Automated fuel/oil/coolant replenishment
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) for:
Remote monitoring (via RS232/computer interface)
Fault diagnostics and protection
Unmanned operation with "five-auto" functionality (start/switch/run/connect/stop)